In the life sciences, maintaining high quality standards is critical not only to the success and sustainability of organizations but also to patient safety and compliance. ISO 9001:2015, part of the ISO 9000 family, provides a robust framework for quality management systems (QMS) that can be used in organizations in the life sciences, including pharmaceutical, natural technology, including medical devices. This article examines the key features of ISO 9001:2015, its benefits, implementation methods, potential pitfalls, and impact in the life sciences.
What is ISO 9001:2015?
ISO 9001:2015 is an international standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS). It outlines criteria for designing a QMS based on several quality principles, including strong customer focus, top management involvement, methodology, and sustainable development. For the life sciences sector, this standard is designed to help organizations ensure that the needs of patients, health care providers, regulatory agencies, and other stakeholders are met while complying with law and regulation of product and service requirements.
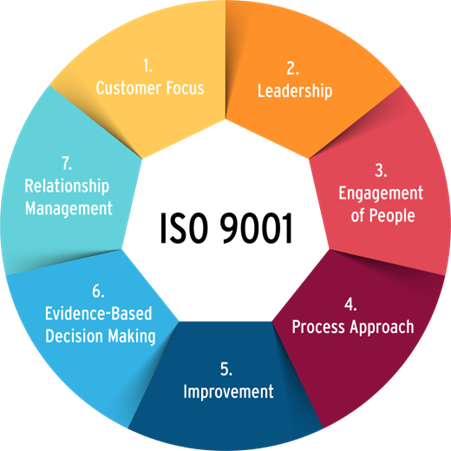
Figure 1: Key Principles of ISO 3001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 is built on fundamental principles that ensure efficient and compliant management systems (QMS). Consumer perspectives are important, including patients, health care providers, and regulatory agencies. Products and services must meet their needs and regulatory requirements, ensuring safety and satisfaction. Leadership requires top management to demonstrate commitment by establishing a clear vision, strategy, and goals that prioritize quality and compliance. People engagement is essential, as skilled and empowered staff are essential to maintain quality and adherence to policies. The process approach involves understanding and managing interconnected processes as a system, improving productivity and efficiency, especially in pharmaceutical and clinical trials. Continuous improvement is a crucial goal in the ever-evolving field of life sciences. Evidence-based decision making ensures reliable outcomes through data analysis, which is essential for clinical research and regulatory compliance. Relationship management is last but not the least, as the company relies heavily on external suppliers, including suppliers and contract review organizations (CROs). Maintaining beneficial relationships with these companies increases the ability to create value and ensure compliance. Together, these principles drive quality and compliance in the life sciences, in line with the highest standards of the industry.
Benefits and pitfalls of ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 has many benefits for the life sciences sector. Enhanced patient safety and satisfaction are primary advantages, as the standard ensures that products and services consistently meet regulatory and customer requirements. By enhancing a process approach, ISO 9001:2015 increases efficiency and reduces waste, which is highly important in environments like pharmaceuticals and medical devices. The standard also regulates systematic risk management, helping organizations minimize adverse effects and ensure product safety and efficacy. Certification to ISO 9001:2015 can enhance an organization’s credibility with regulators and healthcare providers, providing a competitive edge in the market. Additionally, clear communication of processes and objectives, along with employee involvement, boosts job satisfaction and motivation. Implementing ISO 9001:2015 helps organizations consistently meet regulatory requirements, a key aspect in the highly regulated life sciences sector.
However, there can be pitfalls in implementing ISO 9001:2015. Without inadequate commitment from top management, the necessary support and resources may not be available to the QMS, resulting in ineffective implementation. Inadequate training may lead to misunderstanding and non-compliance, as employees may not fully understand the principles and practices of ISO 9001:2015. Inadequate documentation can lead to gaps in the QMS, affecting tracking, auditing, and compliance. Neglecting continuous changes and improvement regarding ISO 9001:2015 can undermine long-term benefits and sustainability. Failure to adequately identify and manage risks can lead to non-compliance and negatively impact product quality and safety. In addition, complicated procedures and documentation can lead to decrease in productivity and increase in employee resistance.
Conclusion
ISO 9001:2015 is not just a set of guidelines; it is a tool that can help organizations in the life sciences improve their overall performance, ensure compliance, and provide a basis for sustainable improvement. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and focus on patient safety and satisfaction, organizations can meet and exceed expectations, thus achieving long-term and sustainable success. However, being mindful of potential pitfalls and actively working to avoid them is critical to realizing the full benefits of ISO 9001:2015 in the life sciences.